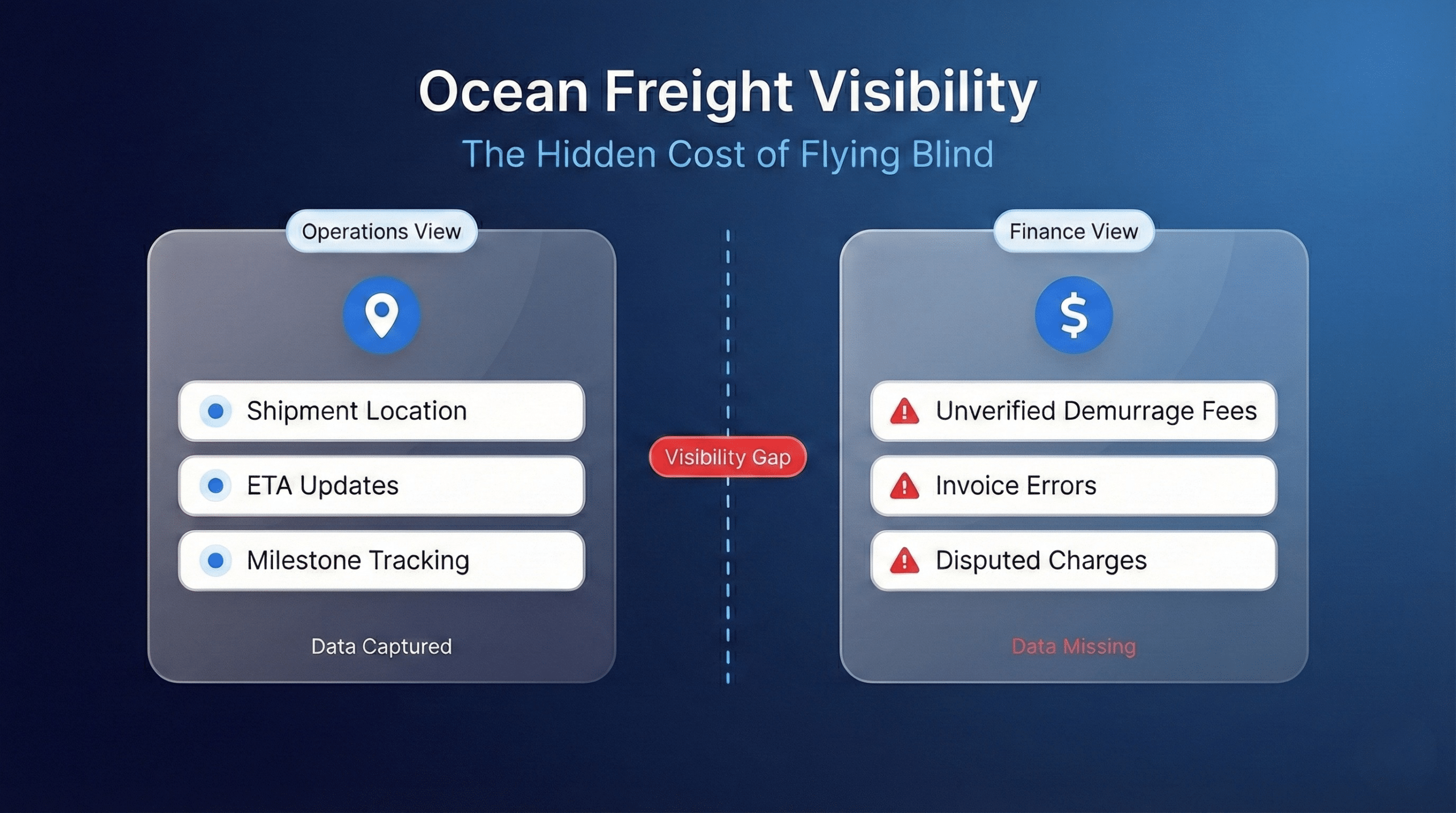
Why do freight billing errors happen?
Freight billing errors cost mid-market shippers 3% to 7% of total freight spend annually. According to Ardent Partners’ 2025 State of ePayables report, 22% of all invoices contain exceptions requiring manual intervention. The most common freight billing errors include incorrect weight or dimensional charges, duplicate invoices, missing discount codes, unexpected accessorial fees, and rate misapplication. Left unchecked, these errors drain cash, damage carrier relationships, and consume accounts payable resources. Below, we break down each error type, explain where it originates, and provide the documentation you need to dispute it successfully.
Key Takeaways:
- 22% of freight invoices contain errors requiring manual correction, costing an average of $53.50 per error to resolve (IOFM, 2025)
- The five most expensive billing errors are weight/dimension discrepancies, duplicate invoices, missing contract discounts, accessorial overcharges, and rate misapplication
- Prevention starts upstream in the warehouse, not downstream in accounts payable
- Winning disputes requires specific documentation: spec sheets, photos, signed accessorial logs, and contract excerpts
Why do freight billing errors happen?
Freight billing errors stem from three root causes: data entry mistakes during invoice creation, misalignment between carrier and shipper systems, and ambiguous contract language that allows interpretation.
Carrier invoices arrive in non-standardized formats, each with unique field names and line item structures. Your ERP may label a service “Call Before Delivery” while the carrier bills it as “Notify Fee.” This translation gap creates confusion and missed audit opportunities. According to the Institute of Finance and Management’s 2025 benchmarks, manual data entry error rates hover around 2% for standard invoices, but freight bills spike higher due to format inconsistencies. Each error costs an average of $53.50 to correct.
Visibility compounds the problem. The Hackett Group’s 2024 Purchase-to-Pay Performance Study found that only 41% of companies have visibility into line-item spend, compared to 93% for top-performing organizations.
What are the 5 most expensive freight billing errors?
The following five error types account for the majority of recoverable overcharges in mid-market freight spend. Each section explains how the error occurs, how to prevent it, and what proof you need to dispute it.
1. Weight and dimension discrepancies
Weight and dimension errors occur when carriers reweigh or re-measure shipments and apply charges higher than the original quote, often due to uncalibrated equipment or missing product specifications.
Carriers audit shipments at terminals using their own scales and dimensioners. If measured weight or dimensions exceed your declaration, the carrier bills at the higher rate. Carrier equipment calibration varies, and your product specifications may not match their measurements.
To prevent these errors, calibrate warehouse dimensioners and scales weekly. Store accurate weight and dimension data for every SKU in your transportation management system (TMS). Photograph shipments at the dock before pickup.
When disputing a reweigh charge, provide the product specification sheet, a calibrated scale certificate from your facility, and dock photos. Carriers are more likely to reverse charges when confronted with manufacturer specifications.
2. Duplicate invoices
Duplicate invoices happen when carriers re-send billing after system glitches, shipment splits, or payment delays, resulting in double payment if your team does not catch them.
These duplicates often appear after carrier system migrations, when shipments split into multiple deliveries, or when delayed payment triggers automated re-invoicing. Because PRO numbers may differ slightly or invoice dates change, duplicates can slip through manual review.
To prevent duplicates, configure your ERP to flag invoices with matching shipment dates, origin/destination pairs, and weight. Cross-reference every invoice against the original PRO number before approving payment.
Disputing a duplicate requires prior payment confirmation, PRO number matching, and shipment date alignment proving the charges reference the same load.
3. Missing contract discounts
Missing discount errors occur when negotiated rates, volume tiers, or promotional pricing fail to apply, often because carrier billing systems are not updated after contract amendments.
You negotiate a 15% discount, sign the amendment, and assume it takes effect. But carrier billing systems operate separately from sales teams. If the rate analyst does not load your new pricing, invoices continue at the old rate. Volume tier thresholds create similar problems when systems do not automatically adjust after you hit qualifying shipment volumes.
Prevention requires quarterly contract-to-invoice reconciliation. Pull sample invoices and verify that applied rates match your signed contract.
To dispute missing discounts, attach the signed contract excerpt with effective dates and volume attestation if applicable.
4. Accessorial charge overages
Accessorial overcharges include fees for services like detention, liftgate, or residential delivery that were either not performed, not pre-authorized, or priced above your contract terms.
Accessorial charges can add 8% to 20% to base transportation rates. Common accessorials include detention, liftgate service, residential delivery surcharges, and appointment fees. Drivers may check boxes for services not actually required, or your contract may specify lower rates than the carrier’s standard tariff.
To prevent overages, require driver signatures on an accessorial authorization log. Train receiving teams to verify services billed match services received. Review contracts to negotiate better accessorial terms before renewal.
Winning disputes requires a signed service log, GPS timestamps proving dock time (for detention), and your contract’s accessorial rate schedule.
5. Rate misapplication
Rate misapplication occurs when carriers bill at incorrect freight class, zone, or base rate, often due to NMFC classification errors or outdated tariff files.
The National Motor Freight Classification system assigns freight classes based on density, handling, stowability, and liability. Incorrect classification at booking or carrier audit means you pay the wrong rate. Zone calculation errors also occur when systems apply incorrect origin-destination mileage bands.
Prevention starts with accurate NMFC classification at shipment. Review product classifications annually, as NMFC codes change. Use automated rate shopping tools to verify quoted rates match contract terms.
To dispute rate misapplication, provide the correct NMFC classification certificate, zone map verification, and your signed contract rate schedule.
How do you dispute a freight billing error?
To successfully dispute a freight billing error, file within the carrier’s claim window (typically 180 days), reference the specific invoice and PRO number, and attach documentation proving the correct charge.
Most carriers accept disputes through online portals, though some require email. Every dispute should include invoice number, PRO number, shipment date, the specific charge disputed, the correct amount, and supporting documentation.
| Error Type | Primary Documentation | Supporting Documentation | Typical Resolution Time |
| Weight/dimension | Spec sheet, certified scale ticket | Dock photo, BOL | 14 to 30 days |
| Duplicate invoice | Prior payment confirmation | PRO match, shipment date | 7 to 14 days |
| Missing discount | Contract excerpt with dates | Volume report | 14 to 21 days |
| Accessorial overage | Signed service log, GPS data | Contract accessorial rates | 21 to 45 days |
| Rate misapplication | NMFC certificate, zone map | Contract rate schedule | 14 to 30 days |
For weight disputes, use language like this:
Sample Dispute Email (Weight Discrepancy) Subject: Dispute Request, Invoice #[NUMBER], PRO #[NUMBER]
We are disputing the weight charge on the above invoice. The billed weight of [X] lbs exceeds our certified product specification of [Y] lbs. Attached: (1) Product spec sheet for SKU [NUMBER], (2) Calibrated scale certificate dated [DATE]. Please reverse the $[AMOUNT] overcharge and issue a corrected invoice.
How can you prevent freight billing errors before they happen?
Preventing freight billing errors requires upstream operational controls, not just downstream AP audits. Warehouse processes, driver documentation, and SKU data accuracy determine whether errors occur.
Top-performing organizations achieve a 99.1% first-time-right invoice processing rate, according to APQC’s 2025 benchmarks. They treat billing accuracy as an operations metric, not just a finance metric.
Use this warehouse prevention checklist:
- Calibrate dimensioners and scales weekly
- Require driver signature for all accessorial services performed
- Verify freight class before tendering each shipment
- Photograph shipments at dock for weight and dimension reference
- Update TMS with accurate SKU dimensions monthly
- Reconcile contract rates against invoices quarterly
If your team lacks bandwidth for manual auditing, consider an automated freight audit. Ardent Partners’ 2024 research found best-in-class organizations reduce invoice processing costs from $12.88 to $2.78 per invoice through automation.
Is freight auditing worth the cost?
For shippers spending $500,000 or more annually on freight, professional auditing typically returns 3% to 7% of total spend in recovered overcharges, far exceeding audit costs.
The choice between in-house and outsourced auditing depends on invoice volume and team capacity. Below 500 invoices monthly, a disciplined internal process may suffice. Above that threshold, manual auditing becomes unsustainable. One global manufacturer recovered over $646,000 by addressing billing and process gaps through systematic auditing.
What else should you know about freight billing errors?
What are the most common freight billing errors?
The most common freight billing errors are weight and dimension discrepancies, duplicate invoices, missing negotiated discounts, accessorial overcharges, and rate misapplication. These five error types account for the majority of recoverable overcharges and typically represent 3% to 7% of total transportation costs.
How do you dispute a freight charge with a carrier?
Submit a written claim to the carrier within 180 days of the invoice date. Include the invoice number, PRO number, and documentation proving the error such as spec sheets, contracts, or photos. Most carriers have online dispute portals that track claim status and response timelines.
What is the difference between a freight bill and a bill of lading?
A bill of lading (BOL) documents shipment details at origin, including weight, piece count, and freight class. A freight bill is the carrier’s invoice requesting payment after delivery. Errors often occur when invoice charges do not match the terms documented on the original BOL.
What are accessorial charges in freight billing?
Accessorial charges are fees for services beyond standard pickup and delivery. Common examples include detention (driver waiting time), liftgate use, residential delivery, inside delivery, and appointment scheduling. These charges are often valid but unexpected when not disclosed upfront during the shipment booking process.
How long do you have to dispute a freight bill?
Most carriers allow 180 days from the invoice date to file a dispute. After this window closes, carriers typically deny claims regardless of merit. Check your specific carrier contracts for exact deadlines, as some impose shorter windows for certain charge types.
What documentation do I need to dispute a reweigh charge?
Provide the product specification sheet showing certified weight, a calibrated scale certificate from your facility, and dock photos if available. Carriers are significantly more likely to reverse reweigh charges when confronted with manufacturer specifications and certified calibration records from the shipping origin.
Freight billing errors are preventable. By understanding where errors originate, documenting proof before disputes, and implementing upstream warehouse controls, you can recover thousands in annual overcharges. If your team lacks bandwidth to audit every invoice, an automated freight audit can reduce risk and recover what you are owed.